Additional Details
PREREQUISITE: This Course Package is appropiate for individuals who meet the qualifications of a Supervisor under Local Law 196.
For More information on NYC Local Law 196, Visit this Page.
Participants need to be able to communicate with the instructor in the language the course is held in.
NYC DOB REQUIREMENT:
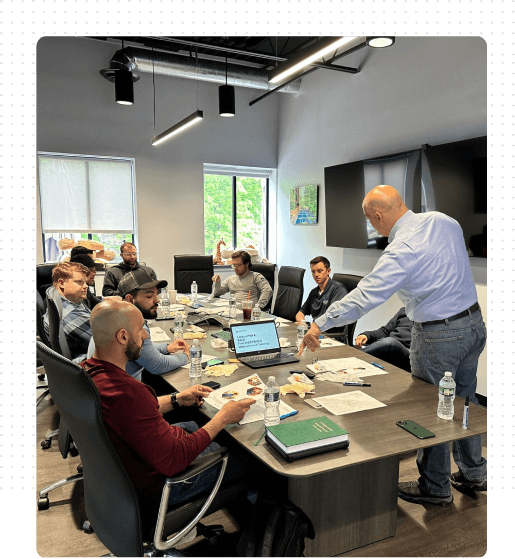
40-HOUR SITE SAFETY MANAGER
New York City’s new requirement beginning July 1st 2016 states that facade projects requiring site-safety plans; buildings 15 stories or higher may now use a site safety manager, who completed construction safety manager training, designated rigging foreman, rigger, or qualified safety professional to oversee site safety on the project.
How to become a safety manager? It is a requirement that the person designated on the project must have the folllowing:
- 40-hour site safety manager training (and 7-hour refresher every 3 years thereafter)
- 32-hour supported scaffold installer training (and 8-hour refresher ever 4 years thereafter)
- 32-hour suspended scaffold supervisor training (and complete the 8-hour refresher every 4 years thereafter)
- OSHA 30 or greater construction training. Minimum 10 hour OSHA every 5 years.
Audience
CEUs (CONTINUING EDUCATION UNITS)
- 4.0
To earn a certificate of completion and a permanent card, student must do the following:
- 100% attendance for the 40 Hour Site Safety Manager Training Course: 40 hours of instruction time
- Completion of Continuing Education and Training Registration Form
- Active participation in all class exercises (determined by instructor)
- Completion of required pre-and post-quiz assessment
- As applicable, achievement of minimum passing score on required end-of-course examination
- Participation and submittal of end-of-course evaluation form (must provide name on form to receive credit)
- Make up time is not allowed. Students who miss time from any individual session must reschedule and attend the full training course.
LEARNING OUTCOMES
Upon completion of this course, student should be able to:
- Explain the differences between the various types of safety professionals
- Recognize rules and regulations and the reasons why they were put into place
- Identify the different types of safety practices and procedures that are put in place to protect the public and property during construction and demolition operations in NYC
- Describe proper communication procedures between licensed safety professionals and the New York City Department of Buildings
- Describe the differences between OSHA standards and NYC DOB Chapter 33 regulations
- Identify potential fire hazards and prevention methods in compliance with the New York City Fire Code
INSTRUCTIONAL METHODS
A plethora of methods will be used, such as auditory and visual methods to ensure learning. This includes the program’s PowerPoint, related lectures, testing, and classroom discussions.
Course Completion Card